- Gender
- Female
Description
Findings:
Primary Preservation Rhinoplasty Z flap technique, Septoplasty, Costal cartilage Graft, Right SEG
Indications:
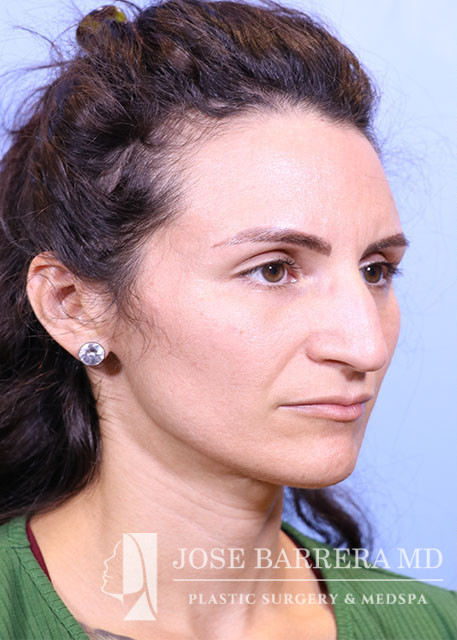
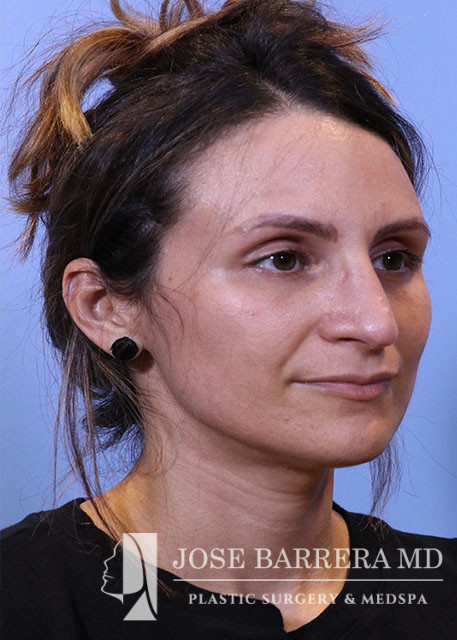
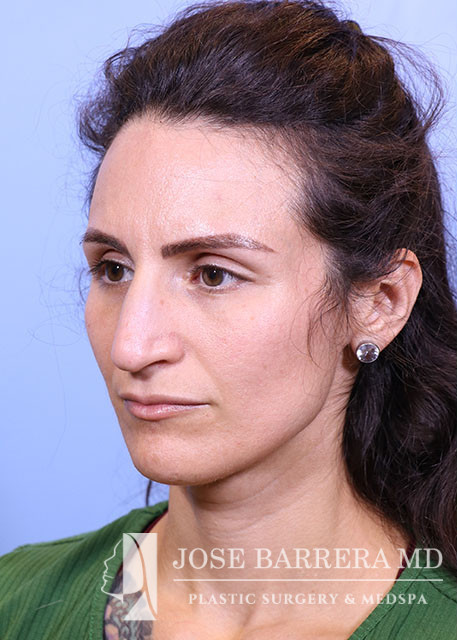
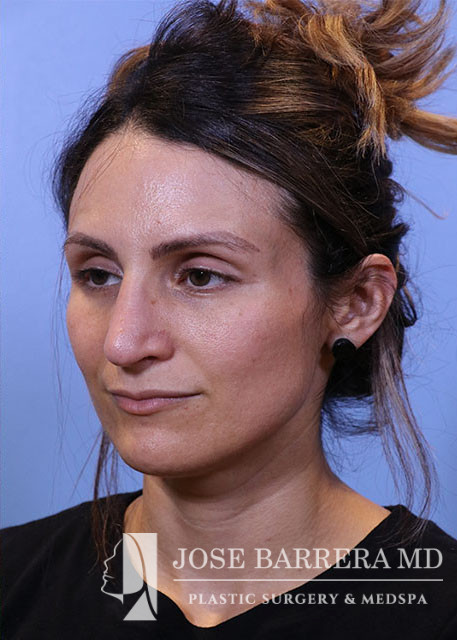
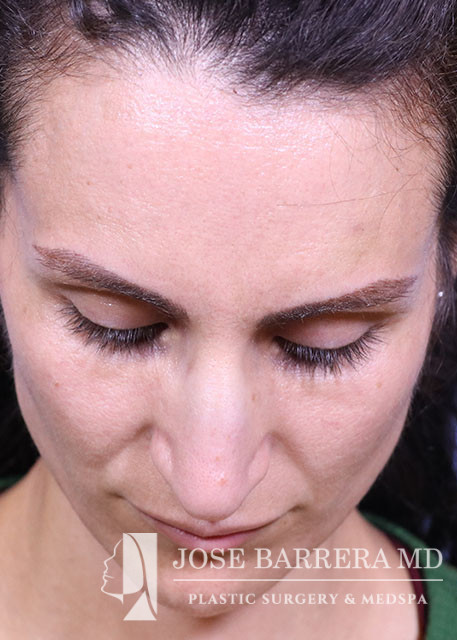
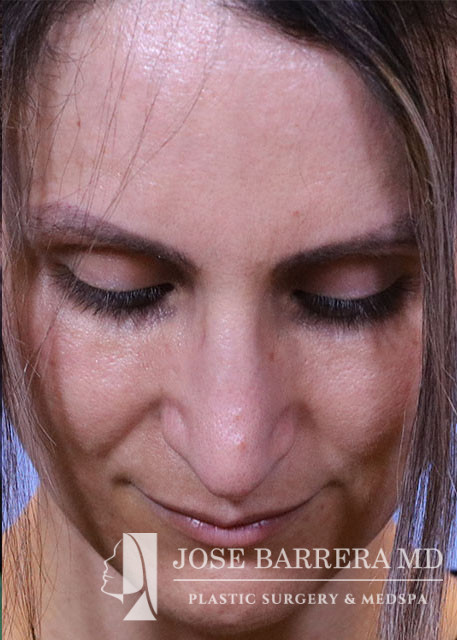
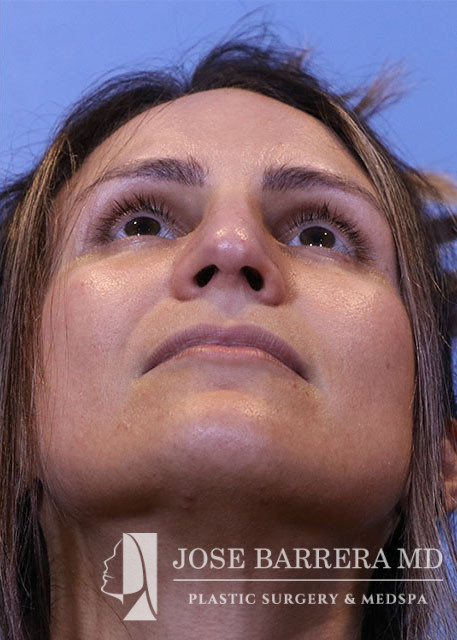
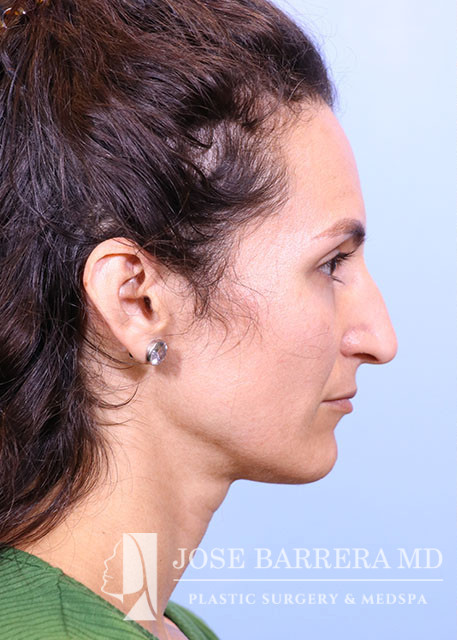
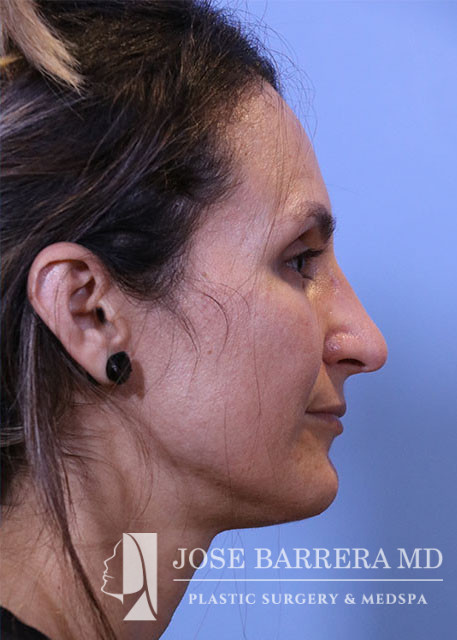
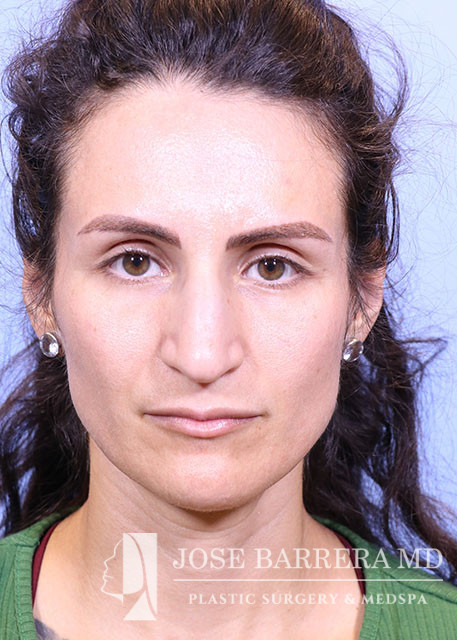
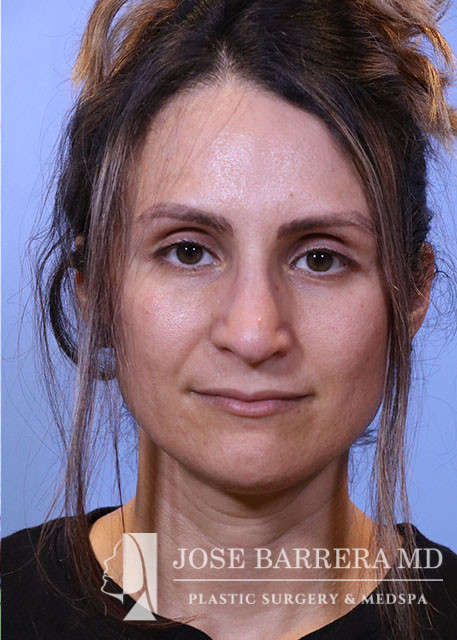
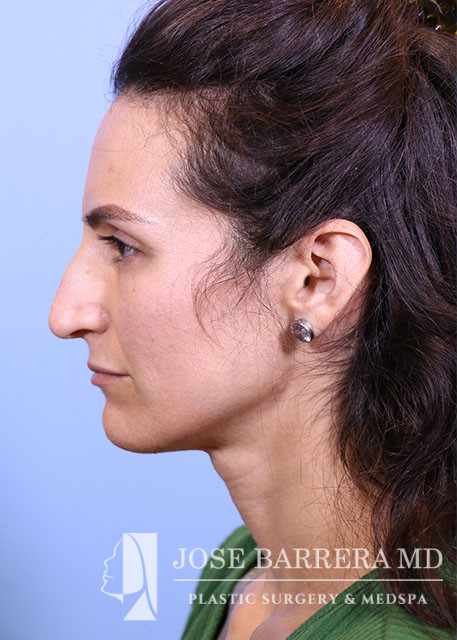
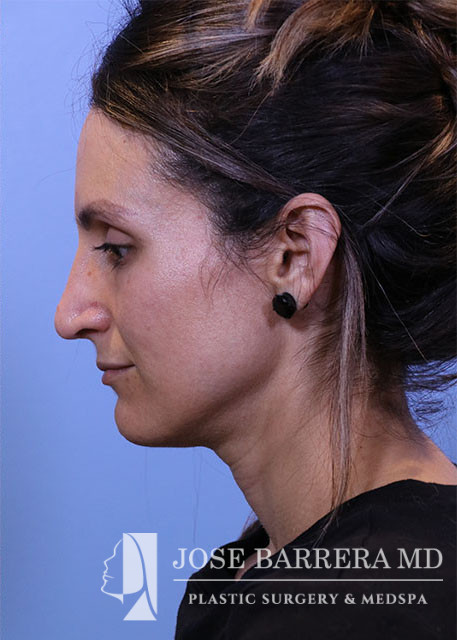
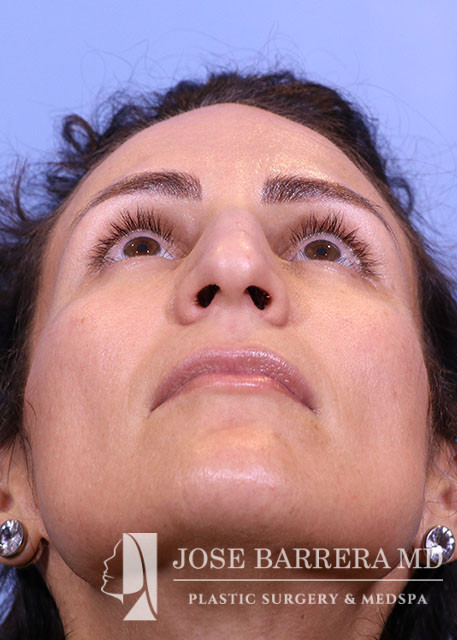
36 year old female with aesthetic nasal concerns. Bothered by her deviated septum and tip ptosis.
Description of Procedure:
Procedure:
Primary preservation open rhinoplasty with Z-flap
Septoplasty
Costal cartilage grafting
Procedure:
The patient was brought to the operating room and identified by name and date of birth. Intravenous anesthesia was administered and an LMA was placed. The nose, pyriform and septum were infiltrated with 1% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine. The patient was prepped and draped in the standard sterile fashion.
An inverted V columellar incision and marginal incisions were marked out and incised. The soft tissue envelope was lifted off the cartilage and bony framework. The periosteum over the nasal bones was incised and elevated.
An incision was then made along the scroll region and the skin and soft tissue were elevated off the maxilla and nasal bones to prepare for osteotomies. The Piezo saw was then used to make low-low-high osteotomies as well as a horizontal osteotomy at the nasion. The dorsal roof remained intact. Small segments of nasal bone were removed at the pyriform aperture to allow for let-down of the dorsal hump. The osteotome was used to contour the wide nasal bones to help narrow them.
The medial crura were separated sharply. The anterior septal angle was identified. A left mucoperichondrial flap was elevated. Dissection proceeded anteriorly around the caudal end of the septum allowing elevation of a mucoperichondrial flap on the right. We elected for a Z flap technique. The point of maximal dorsal convexity was identified and marked. A releasing vertical septal incision was made inferior to the point of maximal dorsal convexity. A modified Z plasty dorsal septum cut was made that connected to the vertical releasing incision. A horizontal osteotomy was made in the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and connected to the transverse osteotomy. Next, the cartilaginous septum was dissociated from the PPE and bony septum. A high wedge of cartilage and PPE were removed allowing for let down. At this point, the nasal dorsum was fully let down. The anterior wedge of cartilage was overlapped on the right side of the native septum. A 5-0 PDS was placed around the mobilized dorsal septum to hold the let down dorsal hump in position. The patient had high septal deviation to the left, so this maneuver also addressed the septal deviation.
Cephalic trims were performed leaving 8mm wide lower lateral cartilages and releasing the scroll. A septal extension graft was fashioned from the costal cartilage and secured to the right side of the native septum with 4-0 PDS and 5-0 prolene. Suture tip contouring was performed and 5-0 prolene dome spanning and lateral crural tensioning sutures were placed to create new domes and increase rotation, securing the lower lateral cartilages to the septal extension graft. The skin was elevated off the medial crura. A tongue-and-groove procedure was performed and the medial crura were sutured to the caudal septum with 5-0 prolene.